At Eduporium, our overarching mission revolves around preparing children for the future. We work with educators to provide affordable access to meaningful technologies that help all students develop the most important hard and soft skills. We also preach about the importance of hands-on, active, and inquiry-based learning experiences. In our view, these are what allow students to see the real world in their learning as much as possible. STEM education is also a huge part of 21st century instruction and we know how important these experiences are. The hard and soft skills students learn throughout elementary, middle, and high school often help them transition into a future career and, for more and more of them, that career might be very closely related to STEM.
Generating Interest in STEM Careers
One reason there are so many STEM jobs is because there isn't enough qualified talent. This is partly due to many children losing interest in STEM early in their lives for a variety of reasons. Some believe they're not smart enough, some fall victim to stereotypes, and others genuinely don't have a desire to pursue it. Of course, this is a bit of a problem because, despite the overwhelming presence of STEM in the modern workforce, there never seems to be quite enough people to fill every job. STEM careers have always been important, however, as professions like doctors, dentists, and scientists are all vital to our society. Now, as computer technology continues to advance and things like AI are more common, it’s more important that people know how to enter some of these emerging STEM fields.
Career fairs and job showcases.
One way educators try to generate more interest in STEM is through school- or district-wide training programs. Similar to internships, career coordinators can set up on-the-job experiences to help students see what STEM professionals might do. STEM has ballooned over the last decade and the careers in this bucket are much more extensive. Educators can use this to their advantage and make it clear that it’s fairly likely students would be able to find a STEM career that aligns with something they're passionate about. They should also stress how STEM work isn't reserved for the smartest of the smart. Sure, intelligence is important, but many of today’s STEM jobs require creativity, collaboration, and analytical skills. Plus, these professionals also need to be willing to make mistakes and solve problems creatively.
New technology means new job opportunities.
If students are willing to put in the work, chances are there's a job in STEM for them. The emergence of new technologies, like 3D printing, for example, have created all kinds of inventive uses for technology. It's relevant in the engineering world, the medical field, in sports, and even in culinary sciences. Yes, science, technology, engineering, and math all collectively make the world a better and more efficient place but we also need people who are skilled in these areas. Different kinds of teaching practices and different kinds of educational experiences can help students open their eyes to the power of STEM learning and hopefully generate that interest in STEM that's sometimes lacking.

Connecting STEM Context and Careers
STEM jobs are among the fastest-growing opportunities across our economy. The amount of STEM-related jobs, in fact, is contributing to the demise of many other traditional careers. These jobs also often come with better pay than many non-STEM jobs that require the same amount of education. Not a ton of college graduates pursue STEM careers either, so you'd think this would encourage students to major in STEM. The prospects of obtaining a high-paying STEM job with less competition is also attractive. Only about one third of undergraduate degree holders over the age of 25, however, have a STEM degree. But, since STEM jobs are growing so rapidly, it’s important to have strong STEM skills. In turn, students will be better equipped to eventually fill these jobs and thrive in the future.
STEM careers and today's booming fields.
The downside surrounding common STEM careers is the large disconnect between available jobs and the number of students pursuing the necessary degrees. Statistics show that, from 2010-20, STEM jobs continued to grow more than jobs in all other fields. The number of jobs in all occupations, for example, increased by 14 percent (prior to the pandemic). Mathematics jobs increased by 16 percent. Computer systems analyst jobs increased by 22 percent. Systems software development jobs increased by 32 percent. Medical scientists jobs increased by 36 percent. And, biomedical engineers jobs increased by 62 percent. This data comes from the U.S. Education Department and indicates that, while job opportunities are trending back up overall, the job opportunities in STEM are booming more so than others.
STEM careers and a bright future.
To help students enjoy STEM and ultimately fill more openings, educators need to help them see the connection between STEM and a promising future. But, at the same time, we're not saying that pursuing a non-STEM endeavor would negatively affect their futures. Simply offering students regular encouragement, however, could affect the likelihood of them pursuing STEM. Graduates can obtain STEM jobs with all sorts of degrees, including Masters degrees, Bachelor’s degrees, two-year degrees, and certificates. With all the available STEM careers and paths for students, it seems there should be more qualified graduates who are ready to step in to these roles but the gap still persists. We can't be certain but it seems relatively likely that generating some more buzz around STEM careers can be one way to inspire students.
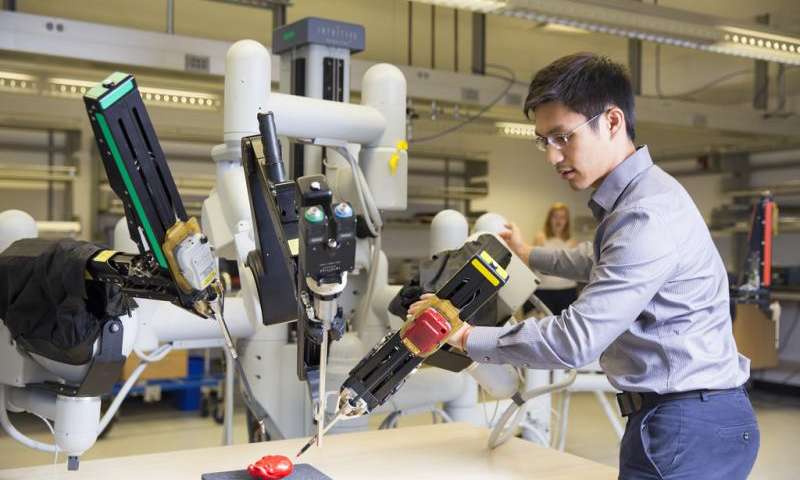
Career Opportunities for Robotics Specialists
STEM careers, as we’ve discussed, are in so many industries and many new ones are still emerging. While it’s not all that new, working in robotics is certainly more prevalent in the last few years. Since learning with classroom robots is great for introducing students to STEM, this could certainly affect how they view the economy. Plus, many teachers see it as a fun way to create hands-on learning. Using robotics in the early grades helps kids learn coding skills and there are other reasons it's beneficial as well. For starters, there's a good chance students will need to be proficient with programming in the future. But, there are other directions these types of careers could take them, too. And, although you could probably identify some examples of robotics use in the real world, there might be many more than you realize.
Career options in STEM and robotics.
The first thing you may think of is a robot exploring another planet, as a concierge worker, or in the military to help diffuse a dangerous situation. In reality, STEM professionals use robots for more than that and, as they continue to advance in efficiency, more uses will emerge. Some of the ways to use robotics include deploying them at opposite ends of the world. Scientists have used robots to explore unreachable depths of the ocean and other hostile environments. One example is using robots to design satellites or rovers that can explore harsh areas of Earth or space. Another niche area is humanitarian robotics. This specific branch involves studying how human interfaces would work with robots or even the ethics involved.
Engineering, research, and career variety.
Not only are robots constantly evolving, the components for constructing them are as well. Some robotics careers now involve designing specialized robot parts, like the gripping technology that allows them to handle items. Robots are also used in the medical field and they need skilled workers to design surgical bots and perform trials. Then, there’s the research side of robotics, which encompasses a great deal of responsibilities. Robotics holds so much potential for maximizing efficiency and optimizing various work environments but we don’t yet know everything about the different methods for engineering, deployment, and consequences. Of course, this makes the research side of things a very intriguing career option (like the rest of these examples) for anyone who's interested in getting more involved with robotics.

Preparing Students for Next-Gen Tech Careers
Technology has helped advanced potential STEM careers to new heights and created completely new job opportunities for today’s students. It also helps advance what educators can provide for these students in the classroom. Internships are also good for students to see how well they do something or learn skills for a particular field. While internship programs aren't available in every high school, however, technology-based learning and CTE are more common. It’s through these kind of hands-on, collaborative, and trial-and-error endeavors that students really learn. Experiential learning is great for discovering potential STEM careers for students who want to solve tomorrow's most complex challenges. It's also key for building the aptitude to develop the necessary skills.
Creating paths to STEM careers.
Giving kids access to purposeful technology is great but their teachers also often need PD courses on integrating and maximizing this technology, especially if they want to illustrate potential STEM careers for kids. If they’re willing to learn, this is very much an option whether they’re just looking to add some hands-on coding to their classrooms or larger scale projects in science labs or makerspaces. Through these learning experiences, educators can create better pathways for students in elementary or middle school to in-demand STEM careers. Making sure students understand how technology could affect their future job prospects is also crucial. And, using this to inspire them to work hard to understand all the ways they could train for some of the highest paying STEM jobs is important as well.
Ensuring opportunities are equitable.
For teachers, priming students for potential future STEM careers starts with instilling the drive to innovate. First and foremost, this often involves shaping their attitudes on preparing for their futures. If more STEM experiences penetrate all schools in all locations and at all economic levels, that would be ideal. Of course, there are also factors beyond what educational leaders can control. The gap that lingers when students can't access to STEM experiences, however, affects their eventual ability to acquire tech jobs. Even without a ton of technology to work with, there are other ways to create impactful experiences. Starting with something simple, like a 3D printer, can create opportunities for students to develop tech skills. It could also help them design solutions and work on developing the exact skills they’ll need for the future.
Preparing Students for Careers in Tomorrow’s Economy
The resources classroom teachers have for preparing students for a possible future in tech aren't always ideal. We understand that school leaders do all they can and sometimes they’re stretched pretty thin when trying to provide innovative learning opportunities for thousands of students. There are some other things they can do, however, that aren’t necessarily completely centered on using technology. A lot of this learning is still hands-on and can definitely give students a leg up in the future. Technology has changed the economy and, in many towns across the country, it's affecting instructional strategies. In agricultural towns, for example, high school students had often been taught farming techniques. Since agricultural work is now largely automated, however, educators have pivoted to teaching students about that technology, including how to control, maximize, and even program it.
Courses with a focus on STEM careers.
Technology classes are now a given in many schools but students don’t always get enough from these opportunities. It depends a lot on the technology they’re using and how it aligns with their skill levels and future challenges. Take elementary students, for example. They’d benefit more from coding with a simple robot than they would from designing a robot. Exposure to technology is a process and it's not necessarily linear. It’s different for every child but one thing that’s at least similar is that it can help them see things in new ways. Ideally, district leaders can provide students with devices for practicing coding in the classroom or at home. Many robotics tools are also compatible with compact devices, which are reasonably priced.
Technology access can benefit everyone.
Using technology throughout their classes also helps improve outcomes for students who are considered impoverished, research has shown. Whether it’s routine access to a computer, learning coding, or even eventually practicing 3D printing, the exposure these students receive can have an enormous impact on their ability to get a tech job. If their school environment isn't ideal for using new technology, however, then the likelihood they develop the necessary fluencies decreases. There is also the certification route, in which students complete relevant certificate programs. These certifications go a long way in helping them break into the tech workforce. They also give them real, on-the-job experiences in many cases. And, since our economy is full of STEM jobs, school leaders should consider doing this for students whenever possible.
For the latest EdTech, STEM, and 21st century education news, follow us on Twitter and Instagram. Like us on Facebook, too, or sign up for our newsletter for announcements on the best EdTech deals around!