It's been a long 15 months since the pandemic upended the education world as we knew it. Aside from forcing teachers into emergency instruction and compelling parents to worry about their child's intellectual and social development, another key factor has emerged. We knew there was a digital divide among our country's students, but we didn't know how bad it really was. As the remote learning era wore on, we learned more about access and equity and these statistics helped provide needed resources for those most deeply affected. But, what's caused this digital divide and have we come out on the other side?
What's Caused the Digital Divide?
There are a lot of factors that have contributed to the digital divide over time. Whatever the case may be, the results include students being unable to develop real-world skills, learn about new technologies, and, ultimately, they lack the opportunities that other students are afforded. It boils down to students (and even their parents) not having adequate access to the Internet and connected devices—or even having no access at all. This is also caused by a number of potential factors. Geographical location is one prime example. Families living in remote areas tend to lack this type of necessary access—something we've seen put under the microscope since the onset of remote learning. Without this access, opportunities for 21st century learning essentially pass some students by.
Some common causes of the digital divide.
Besides geographic factors, there are other reasons—typically out of student control—for this divide. This includes the education level of their parents. Statistics show that college graduates are more likely to go on to enjoy typical access to technologies like the Internet. They're also more likely to enjoy the benefits that technologies like computers provide. In other words, students with parents who haven't always had access to common technology tools are less likely to have the opportunity to build digital literacy themselves. While income levels, geographical location, and digital proficiency can each contribute to the digital divide, it can also sometimes be a lack or parental approval.
Why it's detrimental to students.
Some parents simply don't want their children exposed to technology day in and day out. While misusing technology can certainly have consequences, screen time can yield plenty of positive results as well. Basically, if not exposed to some form of productive technology, children may fall behind their peers. In using it, they can develop simple tech skills and even problem-solving skills depending on how they use it. In any case, the scope of the digital divide has not lessened over time—at least not yet. With the mass availability of electronic devices, you'd think it might be easier to close the gap. As we've seen, however, this could simply result in creating a further divide for those initially impacted anyway.
How the Digital Divide Affects Students
While the digital divide persists, it's tough to make real progress in addressing it. The two most prominent groups of students who suffer from the consequences of the digital divide are those who come from economically disadvantaged families and students of color. The most common impediment created by the digital divide is students being unable to complete homework assignments. As you'd probably expect, many of the homework assignments given to students require the Internet, which presents a problem for those who can't access it. It also plays a role in widening an already problematic divide. Over the last year, however, it exposed an even bigger problem with some students simply unable to access their education.
Enabling learning to continue.
When schools closed down, it wasn't every student who was unable to access computers and the Internet for daily class meetings or to retrieve assignments. Most often, it was students of color and those in low-income families. Of course, distance learning has also required fast Internet for live meetings in most cases—something else that is not a guarantee. Then, there's the devices themselves. As many as 50 percent of students in these two groups didn't have a device for remote learning. This led to school and district leaders spending money on laptops or hotspots and then trying to figure out a way to get them to students—no easy task. While it took incredible time and coordination, it was the only way to ensure every student could keep learning.
Examples of the digital divide affecting students.
Besides facing challenges in connecting with their teachers and accessing assignments, the digital divide can wreak additional havoc for some students. Without similar access, students could wind up falling short of their full academic potential, which has both short-term and long-term effects. In the short term, it could prevent them from learning new things and feeling good about accomplishing tasks. In the long term, they could fall behind peers if they're unable to develop similar competencies. This sometimes leads to another effect—students losing motivation. Knowing that they don't have the same tools as peers can cause some students to withdraw emotionally and check out mentally. Aside from losing out of the convenience technology access provides, these more severe examples could ultimately result in effects that are much tougher to overcome.

Combatting the Digital Divide in Education
In this day and age, it may seem tough to fathom just how many students go without easily accessible technology. As the need to be connected continues to grow, however, the discrepancy remains apparent. Until this gap is eliminated, it will continue to plague everyone involved. Everyone from state and national leaders to parents, teachers, and students themselves are affected by this problem. Going about tightening the gap, however, is not a cut and dry solution. Since different students are affected by the digital divide for different reasons, unique attempts must be made to combat it. In rural areas, for example, the issue is different than it is for students in low socioeconomic areas. Ultimately, it usually comes back to creating greater equity.
Solutions may seem obvious, but are often unattainable.
We're relying on technology more than ever and this is equally true for students. They need it in order to learn new skills, connect with others, and to simply access learning experiences. At the most basic level, the best way to combat the digital divide is to increase technology access. Even if this means increasing technology in public places, like libraries, that's at least a start. A better solution would be to ensure every student has Internet and a reliable device at home. This is, of course, tougher to accomplish, but it's impossible to ignore how those without access to digital tools tend to miss out. Besides that, educators and local leaders can also work together to spread awareness in disconnected communities. This is one way to increase knowledge surrounding this issue and to advocate for technological literacy.
The best opportunities for change.
In order to ensure equal access to technology, it's important to start with economic equality. In low-income households, parents may need help paying for these technologies. Identifying those in need and providing financial assistance is one option. Another is to create and publicize community centers where students could go to access what they need. This would also help community leaders see technology as a necessity rather than a privilege. Finally, it may take more than state and local officials to get the job done. STEM and technology professionals can also play a role. In advocating for the shrinking of the digital divide, they can use their own experiences as an example. Seeing how access can affect so many, it could help create and fuel programs that help students access and leverage technology for better learning experiences.
What We Learned During the Pandemic
The pandemic itself was an enormous learning experience for education officials and, frankly, everyone else involved in homeschooling a student. In fact, it's likely not difficult to find someone who was simply unaware of just how troublesome the digital divide was—either before remote learning efforts began or once they were well underway. Technology was all but essential for a year in order for students to simply receive their education. It wasn't equally accessible, however, and children in low-income and rural communities took the worst of it. Going back to what we've learned, the statistics concerning connectivity are certainly eye-opening. And, more than that, they paint a picture of inequity, struggle, and the absence of solid solutions to the digital divide.
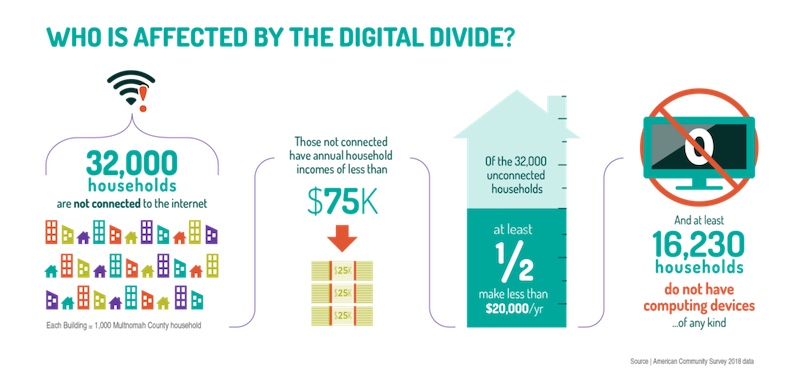
Statistics about connectivity.
With all the focus on ensuring equity, knowing the facts is key. According to FCC officials, 97 percent of US citizens who live in urban areas have easy access to high-speed Internet. This means that students in these locations had a much easier time navigating remote learning. Conversely, only 65 percent of US citizens in rural areas have the same access. On top of that, only 60 percent of people living on tribal lands have that access. This, of course, paints a clear picture of different groups of people with different socioeconomic or ethnic backgrounds enjoying the benefits of digital infrastructure much differently. What's more disheartening is that it's nearly impossible for families in these kinds of situations to make headway. Without reliable Internet access, it's tougher and tougher for them to decrease inequities.
Creating potential solutions.
Despite knowing its impacts, there are still many hurdles to overcome in chasing total equity. One of the potential solutions lies in the development of 5G networks. This, however, is likely to involve government officials and network leaders working together on a long-term solution. With a successful rollout, however, it's likely that all children would benefit from greater access to the technologies they need. It could also lead to greater sustainability and inclusion, especially in the communities most affected. It will take a lot of collaborative effort to really move towards true inclusion, but the presence of emerging technologies is promising. Without connectivity, the digital divide will likely never go away.
Steps to Lessening the Digital Divide for Students
Though the digital divide plagues more than just school-aged children, it's certainly our focus to understand how it affects students. And, don't get us wrong, school leaders have done a lot to minimize or, at least, mask its effects in many cases. Whether it's securing funding for a 1:1 technology plan or working with officials to boost collaboration, we know the intent is certainly there. It typically starts with getting those devices in the hands on students. Then, from there, they need educational software, security software, and communication software. This ensures students can access classroom content in a safe way and share their work with educators for review.
Solutions teachers can try.
One step to decreasing the digital divide is for educators to adjust the resources they use. Of course, many different educational resources these days are electronic. And, many others require Internet access to be viewed. If educators can utilize downloadable materials, however, this could help students with poor or no Internet access. They can also attempt to dole out assignments that don't require the Internet to help foster equity. Additionally, teachers and administrators must be aware of the amount of students who have connectivity issues at home. Knowing this information can factor into how much (and what types) of digital support they provide for them to access while in the school building.
Using all available resources.
Just through regular conversations alone, school administrators are probably aware that educators and parents have tried many creative approaches to combatting the digital divide. There are resources available but, of course, there are also costs. School leaders can try creating community partnerships to help students. At community centers, for example, there is typically Wi-Fi students could access at a place near their home. Whether this is a library or a club, knowing it could be available to them could be a relief for parents and students. Also, some Internet companies offer low-cost access for students in this type of situation. Learning about this option can help administrators provide parents with accurate information and help increase the chances of moving past any digital divide that's lingering.
If you've seen how the digital divide affected students in your school or district at any point during the pandemic, we'd love to hear from you. Feel free to leave a comment below or get in touch with our team to share your story. For the latest EdTech, STEM, and 21st century education news, follow Eduporium on Twitter and Instagram. Like us on Facebook, too, or sign up for our newsletter for our latest product announcements and offerings.



